About HJT
- Current Page >>
- About HJT >>
- About HJT Solar Cell
About HJT Solar Cell
HJT Solar Cell--The Most Potential & Competitive Solar Cell
- Japan Sanyo firstly disclosed a new solar cell structure named HIT (Heterojunction with Intrinsic Thinlayer) in 1990. p-n heterojunction is formed by passivating crystalline silicon cell surface with intrinsic a-Si:H and doped a-Si:H thin film bilayers. The structure avoids direct contact between metal electrode and silicon surface. It is a typical passivated contact solar cell with full area passivated;
- In 2014, Sanyo combined technical advantages of HIT and IBC (Interdigitated back contact) cell features, achieving solar cell efficiency up to 25.6%;
- In 2017, Kanaka improved the efficiency of HBC (Interdigitated heterojunction back contact) cell to 26.7%, which is now the highest efficiency record of crystalline cells.
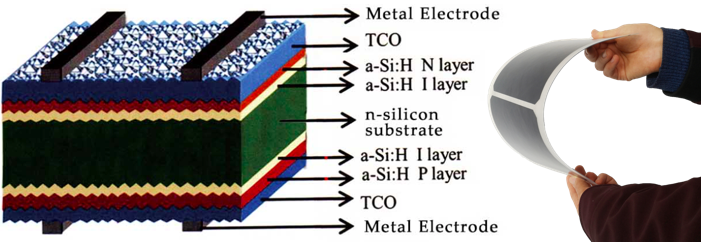
Silicon Heterojunction solar cell (short for “HIT” or “HJT”) combines technical advantages of crystalline silicon cells and amorphous silicon cells. HJT solar cell has low temperature coefficient, excellent weak-light response, high bi-facial power gain and no LID. It can also made by supper-thinner silicon wafer. These features enable it the most potential and competitive crystalline solar cell.
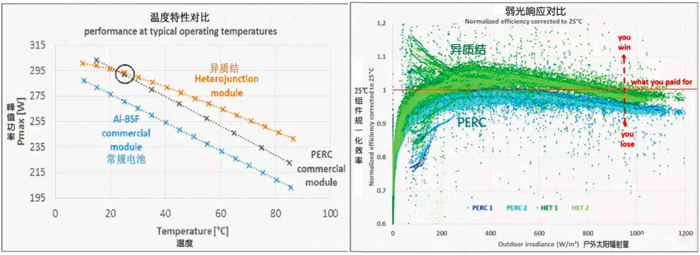
As shown in the left figure below, PERC and HJT panels is with the same rated power of 295W, when tested under the on-site operating temperature (>40℃), HJT panel achieves 5% power gain(Data resource: CEA-INES). As shown in the right figure below, the efficiency data in the scatterplot is the normalized value related to room standard efficiency. The red solid line is the benchmark. It clearly shows HJT panels perform better than PERC Panel(Data resource: CEA-INES).
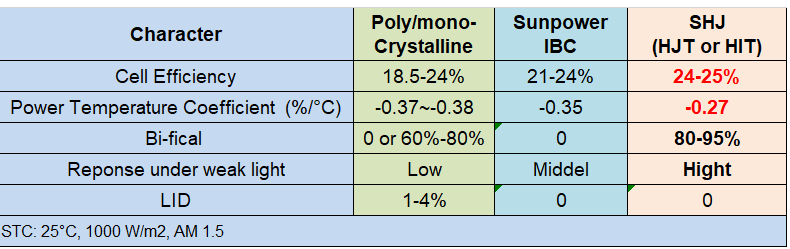
In general, the HJT Solar Cell has the following technical advantages: NO LID&PID, Low Temp. Coefficient, Low Light Performance, Bifacial Power Gain, High Efficiency, Ultral-thin Wafer.
